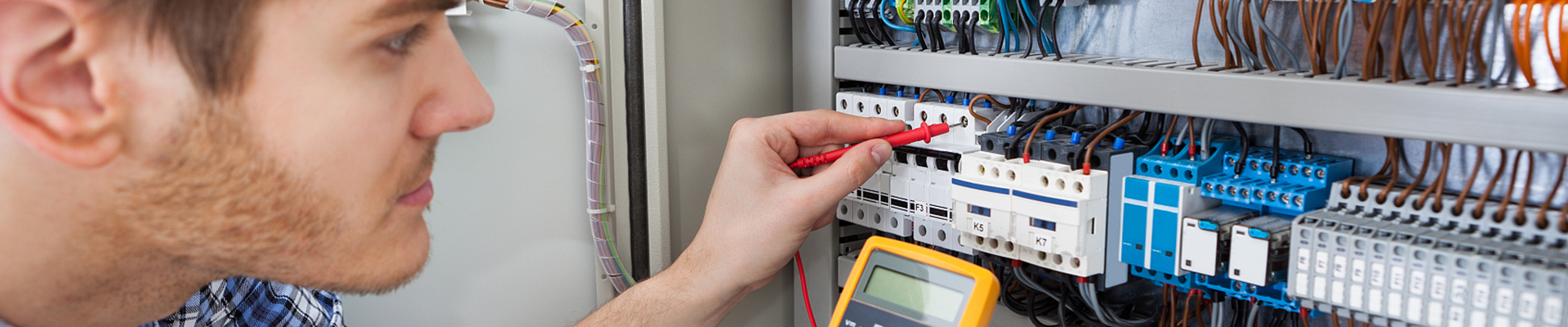
Grounding is one of the most crucial aspects of electrical safety in both residential and industrial settings. Proper grounding ensures that electrical faults, such as short circuits or power surges, are safely directed into the earth, preventing electrical shocks, fires, and equipment damage. To achieve this, specific types of wires are used for grounding purposes. Understanding which wire is best suited for grounding can significantly enhance the safety and longevity of electrical systems.
Types of Wire Used for Grounding
Copper Wire
Copper is the most commonly used material for grounding wires due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Copper grounding wire is highly efficient at transmitting electricity to the ground, minimizing the resistance and ensuring a safe and reliable path for fault currents. It is typically used in both residential and commercial electrical systems and is known for its durability and corrosion resistance. Copper wires are especially ideal in environments where consistent electrical performance is critical.
Aluminum Wire
While copper is the preferred choice, aluminum is also used for grounding, particularly in larger systems. Aluminum grounding wire is lightweight and has a lower cost compared to copper, making it a cost-effective alternative for large-scale industrial applications or long-distance grounding systems. However, aluminum has a higher resistance than copper, which means that it may require larger gauge sizes to achieve the same performance level. In addition, aluminum can corrode over time, so proper maintenance and regular inspections are essential.
Copper-Clad Aluminum Wire
For applications that require a balance of cost-effectiveness and performance, copper-clad aluminum wire can be an excellent choice. This wire features a core of aluminum with a copper coating, combining the lightness of aluminum with the high conductivity of copper. Copper-clad aluminum is increasingly popular in situations where cost is a major concern but reliable performance is still required. It's commonly used in telecommunications and electric power distribution.
Steel Grounding Wire
While not as common as copper or aluminum, steel wire is sometimes used in grounding applications, particularly when additional strength and durability are needed. Steel is typically used for grounding rods and earthing systems, where physical strength and longevity are priorities. However, steel has lower conductivity compared to copper and aluminum, which is why it is less frequently used for direct electrical grounding.
Galvanized Steel Wire
Galvanized steel wire is steel wire coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. This type of wire is commonly used in industrial applications, such as fencing or earth grounding systems where rust resistance is needed. It is not as electrically conductive as copper but can be an affordable solution when cost is a consideration.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Grounding Wire
When selecting the appropriate wire for grounding, several factors should be taken into account:
Conductivity: Copper and copper-clad aluminum offer the best conductivity for efficient fault current dissipation.
Corrosion Resistance: Copper and aluminum are both resistant to corrosion, though copper offers a higher level of protection, especially in damp or corrosive environments.
Cost: Copper is the most expensive, while aluminum and copper-clad aluminum offer more affordable options for larger installations.
Environmental Conditions: For outdoor or industrial applications, corrosion-resistant wires, such as copper or galvanized steel, are often preferred due to exposure to moisture or chemicals.
Why Proper Grounding Matters
The primary purpose of grounding is to ensure electrical safety by providing a direct path for fault currents to safely reach the earth. Without proper grounding, there’s a risk of electric shock, electrical fires, and damage to electrical appliances. Inadequate grounding can also result in system malfunctions, especially in sensitive equipment, making the choice of grounding wire critical to the long-term reliability of an electrical system.
In conclusion, copper remains the most widely used wire for grounding due to its superior conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion. However, depending on the size, cost considerations, and specific environmental conditions, aluminum, copper-clad aluminum, and galvanized steel wires may also be used. Ensuring the correct type of wire is used for grounding is essential for maintaining the safety, efficiency, and reliability of electrical systems. Whether you're working on residential, industrial, or large-scale electrical installations, choosing the right grounding wire will protect both people and property from electrical hazards.
 English
English  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  français
français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ไทย
ไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা
বাংলা  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türk
Türk  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  عربى
عربى  norsk
norsk  اردو
اردو  čeština
čeština  Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά  Українська
Українська  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  ລາວ
ລາວ  Қазақ
Қазақ  Euskal
Euskal  slovenský
slovenský  Македонски
Македонски  Română
Română  Српски
Српски  简体中文
简体中文  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  עִברִית
עִברִית  יידיש
יידיש  Беларус
Беларус  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  հայերեն
հայերեն 






