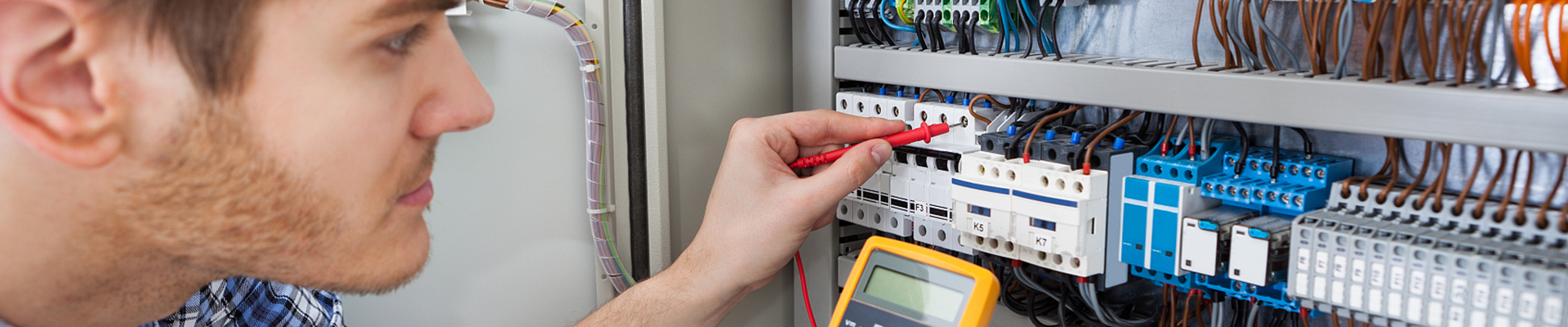
Grounding is one of the most crucial elements in electrical safety, ensuring that electrical systems remain secure and functional under a variety of conditions. Proper grounding helps prevent electrical shocks, reduces the risk of fire, and protects both equipment and people from electrical faults. To achieve this, specific types of wire are used for grounding, each designed to handle different requirements. Understanding which wire to use for grounding can make a significant difference in the safety and longevity of your electrical system.
Common Types of Grounding Wire
Copper Wire
Copper is the most widely used material for grounding wire due to its excellent conductivity. It provides an efficient path for fault currents to flow into the ground, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards. Copper grounding wire is highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions. Its high conductivity ensures that it remains an optimal choice for residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems. Although copper tends to be more expensive than other materials, its performance and reliability justify the cost in most applications.
Aluminum Wire
While copper remains the standard, aluminum wire is often used as a more cost-effective alternative for grounding, especially in larger, more extensive electrical systems. Aluminum is lightweight and less expensive than copper, which makes it an attractive option for utility companies and industrial applications. However, aluminum has a higher resistance than copper, meaning it may require larger gauge wire to achieve the same conductivity. Despite being less conductive, aluminum can still be a reliable choice when appropriately sized, but it does require careful maintenance and periodic inspections to prevent issues like oxidation.
Copper-Clad Aluminum Wire
For those looking for a balance between cost and performance, copper-clad aluminum wire offers a practical solution. This wire features an aluminum core with a thin copper coating, combining the best of both materials. The copper coating provides excellent conductivity, while the aluminum core reduces the weight and cost of the wire. Copper-clad aluminum is commonly used in telecommunication systems and power distribution networks, where both cost savings and reliable performance are essential.
Galvanized Steel Wire
Though less common for direct electrical grounding, galvanized steel wire is sometimes used in specialized applications. Steel wires are often used for grounding rods or in earth grounding systems because of their strength and ability to withstand physical stresses. Galvanizing the steel with a layer of zinc protects it from rust and corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor or industrial environments. However, steel has much lower electrical conductivity compared to copper or aluminum, so it’s typically used in combination with other materials or for structural grounding rather than direct electrical fault protection.
Choosing the Right Grounding Wire
When selecting the appropriate wire for grounding, several factors must be considered:
Electrical Conductivity: Copper is the best conductor, but aluminum and copper-clad aluminum are also reliable options.
Corrosion Resistance: Copper and galvanized steel offer superior corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity in harsh environments.
Cost Efficiency: Aluminum and copper-clad aluminum provide more affordable options, making them popular for larger applications.
Application Type: For residential systems, copper is often preferred, while aluminum or steel may be used in industrial or utility applications.
The Role of Grounding in Electrical Safety
The primary role of grounding is to provide a safe path for electricity in the event of a fault, directing any unwanted electrical current away from sensitive equipment and structures. Without a proper grounding system, electrical systems can become dangerous, potentially leading to electric shocks, fire hazards, and damage to appliances. Grounding wire, therefore, is not just a technical requirement but a crucial safety measure that can prevent costly accidents and injuries.
In conclusion, choosing the right grounding wire is essential for maintaining the safety and reliability of any electrical system. While copper remains the top choice for its unmatched conductivity and durability, aluminum and copper-clad aluminum provide viable alternatives at a lower cost. Galvanized steel, though less conductive, offers additional strength for structural grounding purposes. Regardless of the material, proper installation and maintenance of grounding wire are vital for ensuring the effectiveness of the system. As electrical systems grow more complex, the demand for high-quality grounding solutions will continue to rise, making it important to understand the various wire types and their applications.
 English
English  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  français
français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ไทย
ไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা
বাংলা  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türk
Türk  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  عربى
عربى  norsk
norsk  اردو
اردو  čeština
čeština  Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά  Українська
Українська  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  ລາວ
ລາວ  Қазақ
Қазақ  Euskal
Euskal  slovenský
slovenský  Македонски
Македонски  Română
Română  Српски
Српски  简体中文
简体中文  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  עִברִית
עִברִית  יידיש
יידיש  Беларус
Беларус  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  հայերեն
հայերեն 






